This article is not part of the System Center Cloud series but we will use the final product to host System Center database instances.
Low-level design
Service accounts, user accounts and groups
Pre-create another set of service accounts that will be used for the new instance in the Active Directory. It is best practice to have separate accounts for each instance.
SQL DB Servers – Service accounts
- sercontsqlfcic0dp0a
- Service account: SQL Server Agent
- Member Of
- Domain Users
- sercontsqlfcic0dp0d
- Service account: SQL Server Database Services (Database Engine)
- Member Of
- Domain Users
- sercontsqlfcic0dp0sr
- Service account: Reporting Services
- Member Of
- Domain Users
Storage
- You will need another cluster disks and Mount Point disk if you decide to use it.
Install another instance of Microsoft SQL Server on the first node of the Failover Cluster
The installation of the another clustered instance is similar to the installation process of the first instance.
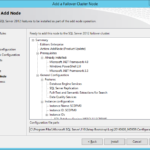
- New SQL Server failover cluster installation
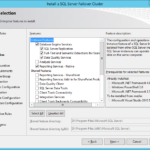
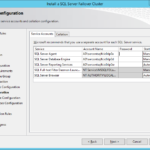
- Select same or different features.
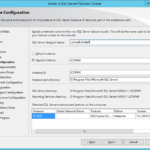
- Specify name of the new SQL Server cluster that will reside on this Windows Server 2012 R2 cluster.
- Set name of the new instance and change the root directory if you want to separate OS and applications (SQL Server).
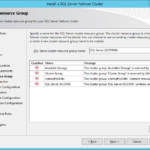
- Name of the SQL Server cluster resource group have to be different.
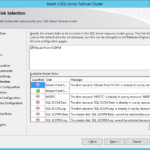
- Set your new cluster disks or Mount Point disk if you decided to use it.
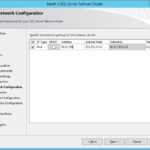
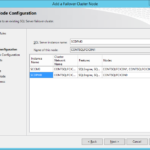
- Set IP address.
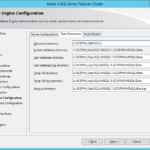
- New service accounts.
- Paths will be different. Do not forget to set paths to another directory under the mount point as I explained in the previous article.
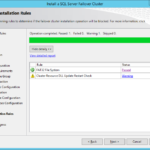
- Install
Configurations after installation
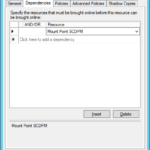
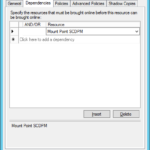
Configure dependencies in the Failover Cluster Manager
Install another instance of Microsoft SQL Server on the second node of the Failover Cluster
Verify the installation
- Same process like it was noted in the previous article.